Understanding How Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers (GPHEs) Work
Plate heat exchangers are vital in many industries’ heat transfer processes. This article delves into how gasketed plate heat exchangers work, exploring their working principles, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. If you’re in the field of HVAC, engineering, or any sector that requires efficient heat exchange, understanding these systems can significantly impact your work. Read on to uncover the intricacies of these heat exchangers and how they can be optimised for various applications.
Outline
- What is a Plate Heat Exchanger?
- How Does a Gasketed Plate Heat Exchanger Work?
- Different Types of Plate Heat Exchangers
- Advantages of Plate Heat Exchangers
- Disadvantages of Plate Heat Exchangers
- Gasketed Plate Heat Exchanger vs. Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
- Critical Applications of Plate Heat Exchangers
- Understanding the Working Principle of Plate Heat Exchangers in HVAC
- Selecting the Right Plate Heat Exchanger for Your Needs
- Maintaining and Troubleshooting Plate Heat Exchangers
What is a Plate Heat Exchanger?
A plate heat exchanger is designed to transfer heat between two fluids without mixing them. These exchangers consist of multiple thin, corrugated metal plates, which create channels for the fluids to flow through. The unique design of these plates increases the heat transfer surface area, enhancing the efficiency of the heat exchange process. The primary components of a plate heat exchanger include heat transfer plates, gaskets, a frame, and tightening bolts.
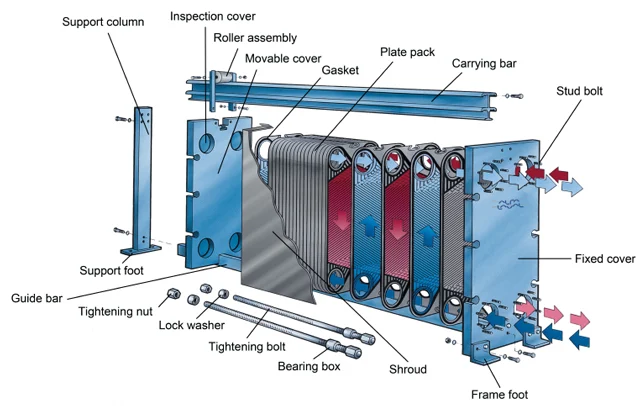
How Does a Gasketed Plate Heat Exchanger Work?
A gasket plate heat exchanger operates on a straightforward yet highly effective working principle. The exchanger consists of a series of metal plates sealed with gaskets. These gaskets direct the fluid flow and prevent leakage. Hot and cold fluids pass through alternate channels formed by these plates. The high surface area of the plates allows for efficient heat transfer between the fluids, driven by the temperature difference between them. The plates are compressed by tightening bolts, ensuring a secure fit and optimal heat exchange.
Different Types of Plate Heat Exchangers
There are several types of plate heat exchangers, each designed for specific applications:
- Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers: These are versatile and easy to maintain, with gaskets sealing the plates and directing fluid flow.
- Brazed Plate Heat Exchangers: Compact and robust, ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
- Welded Plate Heat Exchangers: Suitable for aggressive fluids and extreme conditions, with welded joints replacing gaskets.
- Semi-Welded Heat Exchangers: A hybrid design combining welded and gasketed plates, offering a balance of strength and flexibility.
Advantages of Plate Heat Exchangers
Plate heat exchangers offer several advantages:
- High Heat Transfer Efficiency: The corrugated design of the plates provides a large surface area for heat transfer, resulting in high efficiency.
- Compact Size: These exchangers are smaller and lighter than traditional shell and tube heat exchangers, saving space.
- Flexibility: Plates can be added or removed to adjust capacity, making them versatile for various applications.
- Easy Maintenance: The design allows easy cleaning and inspection by removing the plates.
Disadvantages of Plate Heat Exchangers
However, plate heat exchangers also have some disadvantages:
- Pressure Drop: The complex flow paths can result in a higher pressure drop than other heat exchangers.
- Fouling: The narrow channels between plates can become fouled more quickly, requiring regular maintenance.
- Gasket Wear: The gaskets can degrade over time, especially in high-temperature or aggressive fluid applications, necessitating replacements.
Gasketed Plate Heat Exchanger vs. Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
When comparing gasketed plate heat exchangers to shell and tube heat exchangers, several factors come into play:
- Heat Transfer Efficiency: Plate heat exchangers typically offer a higher heat transfer coefficient due to the larger surface area.
- Size and Weight: Plate heat exchangers are more compact and lighter, making them easier to install and maintain.
- Maintenance: Shell and tube heat exchangers might be easier to clean for heavily fouled fluids, but plate heat exchangers allow quick access and inspection.
Critical Applications of Plate Heat Exchangers
Plate heat exchangers are used in a variety of industries:
- HVAC Systems: For efficient heating and cooling processes, plate heat exchangers’ high heat transfer capabilities are utilised.
- Food and Beverage Processing: To ensure safe and efficient pasteurisation and sterilisation.
- Chemical Processing: For handling aggressive fluids and maintaining precise temperature control.
- Renewable Energy: In heat recovery systems, it maximises energy efficiency.
Understanding the Working Principle of Plate Heat Exchangers in HVAC
In HVAC systems, the working principle of plate heat exchangers is crucial for efficient heat transfer. The design of the plate and frame heat exchanger allows for effective heat transfer between air handling units and the external environment. By leveraging the temperature difference between indoor and outdoor air, HVAC systems can maintain optimal indoor temperatures while minimising energy consumption. The compact design of these exchangers fits well within the confined spaces of HVAC installations.
Selecting the Right Plate Heat Exchanger for Your Needs
Choosing the suitable plate heat exchanger involves considering several factors:
- Fluid Types: The chemical properties and temperature of the fluids being used.
- Flow Rates: The required flow rates for both hot and cold fluids.
- Pressure and Temperature Conditions: Maximum operating pressure and temperature requirements.
- Maintenance Requirements: Ease of maintenance and cleaning based on the application’s fouling potential. Consulting with experts or using selection software can help determine the most suitable plate heat exchanger for your specific needs. For detailed guidance, refer to resources like Virdis Energy.
Maintaining and Troubleshooting Plate Heat Exchangers
Proper maintenance of plate heat exchangers ensures long-term efficiency and reliability:
- Regular Inspection: Check for gasket wear, corrosion, or fouling signs.
- Cleaning: Periodic cleaning to remove deposits and prevent fouling.
- Gasket Replacement: Replacing gaskets to maintain a proper seal and efficient heat transfer.
- Monitoring Performance: Keeping track of pressure drops and temperature differences to detect any performance issues early.
Summary
- Plate heat exchangers are efficient devices for transferring heat between two fluids without mixing them.
- Gasketed plate heat exchangers use gaskets to seal and direct fluid flow through corrugated metal plates.
- They offer high heat transfer efficiency, compact size, and flexibility but can suffer from pressure drops and fouling.
- Understanding their working principles, especially in HVAC systems, is crucial for optimising performance.
- Selecting a suitable heat exchanger requires careful consideration of fluid properties, flow rates, and operating conditions.
- Regular maintenance is essential to prevent fouling and ensure longevity.
For further information and expert guidance, explore resources like Virdis Energy, which provides comprehensive insights into heat exchanger technologies.














